Security Risk Management When Using Cloud Computing (Part 2)

In April 2020, the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) issued a joint statement to highlight security risk management practices for cloud computing services. The statement focused on five key areas: governance, cloud security management, change management, resilience and recovery, and audit and control assessments. Within these five areas the FFIEC provides best practices and other control considerations to help identify, manage, and monitor risk to financial institutions (FI) using cloud service providers. Although FIs have a strong track record of effectively managing their systems, the use of cloud service providers can introduce new subtleties. We encourage FIs review this brief summary of how the FFIEC suggests FIs should approach each of the five key areas to help ensure a thorough consideration, paying particular attention to areas that stress FI responsibilities.
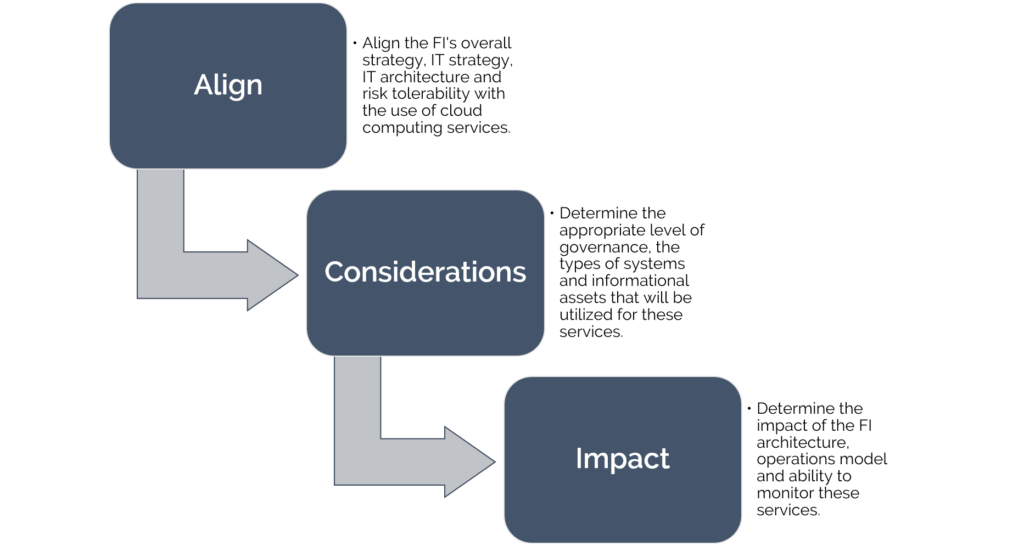
Governance
FIs should consider the following risk management practices regarding governance when considering migrating to the use of cloud computing services:
Cloud security management
Consider the following categories of controls and processes related to managing the security of your cloud computing environment:
Risk management
When implementing risk management practices for your cloud computing environment, the following steps should be considered:
- Identify security related risks during the planning, implementation, and selection of a cloud service provider.
- Implement appropriate control processes to mitigate identified risks once an agreement is in place.
- Identify control effectiveness by testing or auditing the cloud service provider’s security controls. This can be done by leveraging a System and Organization Controls (SOC) report.
- Implement and monitor the security tools and configuration management capabilities provided by the cloud service provider to ensure that all risks are mitigated.
Inventory identification and management
Consider the following processes related to inventory identification and management:
- Determine the information and system types that will be migrated to your cloud computing environment.
- Create inventory management procedures to account for all systems and information; including virtual machines, firewalls, and network devices to ensure better management and safeguarding of information.
User access provisioning and permission levels
The set-up of system users and permission levels is vital to the security of a cloud computing environment. The following processes should be considered for implementation to address user provisioning and permissions.
- Create defined processes for creating, modifying, and deleting user accounts.
- Establish permission levels based on job function, applying the principle of least access privileges.
- Limit elevated privileges to only those deemed necessary and use multi-factor authentication for these accounts.
- Create separate user accounts for elevated users to further segregate and monitor high-level functions.
- Review user access and permissions, including elevated accounts, on a regular basis.
- Monitor the activity of elevated accounts on a regular basis.
- Change all default access credentials.
Data loss prevention
The following processes should be considered for implementation with respect to data loss prevention.
- Implement encryption and data tokenization where applicable.
- Create a defined process for encryption key management between the cloud service providers and FI. Encryption key management systems are often offered by the cloud provider but beware that they may allow access to the information by an administrator from the cloud provider.
- Establish clear communication between both parties to identify the best controls for protection of sensitive data
End user training
Even with proper security configuration within your cloud computing environment, end users still have a significant impact on its security. The FI should seek out trainings specific to the cloud environment and require attendance by all users. Trainings can be obtained from external organizations or may consist of product specific trainings provided by the cloud service provider.
Change management
Effective change management policies and procedures are important when transitioning to a cloud computing environment. Consider implementing the following processes related to change management and the software development life cycle.
- Establish documented, detailed change management procedures that encompass software development activity. While the FI may already have these in place, they should be reviewed and revised to include procedures for the cloud computing environment.
- If the FI employs a microservice architecture, ensure that established change management procedures are implemented throughout the entire environment to include all microservices.
Resilience and recovery
In regards to managing resilience and recovery of the cloud computing environment, consider implementing the following processes:
Business continuity and disaster recovery
- Review the resilience capabilities and service options available from the cloud service provider to determine what services are included in the original contract or if additional services are necessary.
- Evaluate the effect of the resiliency services provided on the FI’s current business continuity and disaster recovery plan and incorporate changes based on the identified responsibilities of the FI and the cloud service provider established in the contract.
- Ensure procedures are in place to update resiliency plans and perform tests of these procedures on a regular basis.
Incident response capabilities
- Review the cloud service provider’s contract to identify the responsibilities of both the FI and the provider specific to the identification, response, remediation, and communication to reported incidents.
- Review and revise established internal incident response procedures to include the responsibilities of the FI and service provider to ensure there is a clear understanding of how each should respond to a reported incident.
Audit and controls assessment
Even with thorough due diligence and validation of strong controls upon implementation, there is a risk of controls not being implemented consistently or deteriorating over time. To address managing audit and control assessments, consider the following processes pertaining to both internal monitoring at the FI and the FI’s responsibility for monitoring its cloud service provider:
Internal monitoring
- Establish practices with external assessors or the internal audit function to perform regular audit and testing of security controls that have been implemented to secure the cloud computing environment.
External monitoring
- Evaluate and monitor the cloud service provider’s technical, administrative and physical security control environment that is used to support the FI’s cloud computing services. This can include reviewing internal assessments and security reports and implemented policies and procedures such as internal audit reports, penetration testing, and vulnerability scans, written information security plans, and business continuity and disaster recovery plans.
- Establish practices for obtaining and reviewing external audit reports of the cloud computing services, including SOC reports and ISO certification reports, to gain assurance that controls within the cloud service provider are implemented and operating effectively.
Cloud services can be beneficial to FIs if the risk is properly managed. By considering the implementation of identified controls and processes recommended by the FFIEC, FIs can help ensure they have implemented sound risk management over their cloud computing services.
If you would like to discuss these matters further, contact your BNN advisor at 800.244.7444.
Disclaimer of Liability: This publication is intended to provide general information to our clients and friends. It does not constitute accounting, tax, investment, or legal advice; nor is it intended to convey a thorough treatment of the subject matter.




